The algorithm is known for its efficiency in complexity (time and memory) and for sorting lists:
- We cut the data into two equal parts.
- We sort the data of each part (we split each part, the algorithm becomes recursive).
- We merge the two parts.
We recursively currency the starting array into two subarrays until the array contains only one element. Once the elements are sorted independently of each other, from that point on, the backtracking starts and we're going to merge the subtables into one until you get the sorted starting board. The merge consists of successive comparisons.
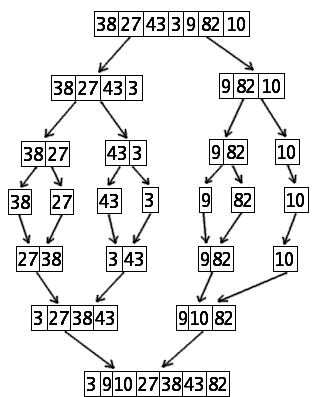
Example
Suppose we want to sort the following table: [ 38, 27 ,43, 3, 9, 82, 10]
Algorithm
TriFusion ALGORITHM(T, left, right);
T: table of values;
left,right: integer;
center: integer;
TOP
IF (left < right) THEN
← center (left + right) / 2;
TriFusion (T, left, center);
TriFusion (T, center + 1, right);
MERGE(T, left, center, right);
FSI
FIN.
Commentaires (0)
Laisser un commentaire
Connectez-vous pour commenter
Rejoignez la discussion et partagez vos connaissances avec la communauté
Chargement des commentaires...